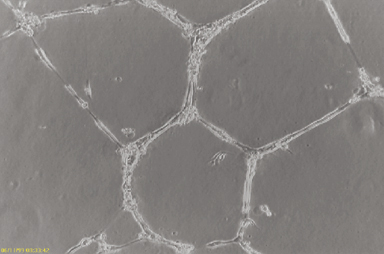
HUVEC Tube Formation on ECM Gel. HUVEC cells from a standard tissue culture plate were incubated on an ECM gel. After several hours, tube formation can be visualized under a light microscope.

| Catalog Number | CBA-200 |
|---|---|
| Size | 50 assays |
| Detection | Light Microscopy |
| Manual/Data Sheet | Download |
| SDS | Download |
Product Details
For angiogenesis to occur, endothelial cells must escape their stable location and break through the basement membrane. Cells migrate toward an angiogenic stimulus that may be released from nearby tumor cells. These cells proliferate to form new blood vessels.
Our Endothelial Tube Formation Assay (In Vitro Angiogenesis) provides an easy, robust system to assess angiogenesis in vitro. The ECM gel matrix very closely resembles an in vivo environment.

HUVEC Tube Formation on ECM Gel. HUVEC cells from a standard tissue culture plate were incubated on an ECM gel. After several hours, tube formation can be visualized under a light microscope.
상품문의가 없습니다.
추가비용을 고객에게 부담시지키 않습니다. (단, 고객 변심 또는 주문 반복으로 인한 경우의 반환비용은 고객님이 부담하셔야
합니다.)
::: 교환 및 반품이 가능한 경우:::
단, 상품을 개봉하여 상품가치가 상실된 경우에는 교환/반품이 불가능합니다.
:::교환 및 반품이 불가능한 경우:::
주문 취소 및 반품으로 환불을 요청하실 경우에는 E-mail(celgen-bio@celgen-bio.com)이나 고객만족센터 (042-824-9026)을
통해 요청하시면 친절하게 처리해 드리겠습니다.
주문 취소 후 반품 가능 여부를 확인한 다음 3일 이내에 결제 금액을 환불해 드리겠습니다.